
Loan Origination Software for MSME Lending: A Practical Guide for Indian Banks & NBFCs

Loan Origination Software for MSME lending is where your unit economics are won or lost. The constraint for Indian banks and NBFCs isn’t capital—it’s origination. Small tickets, heterogeneous borrower profiles, and tight regulatory expectations turn paper-heavy onboarding and fragmented checks (GST, bank statements, bureaus) into slow, costly journeys.
A modern Loan Origination Software (LOS) built for India fixes this at the root. You standardize journeys while allowing segment-level variation: single-capture KYB/KYC reused across products; direct integrations with GSTN, Account Aggregator, CKYC, PAN/MCA, and Udyam; automated bank-statement parsing and cash-flow analysis; configurable scorecards and policy rules that mirror your credit framework. Add eSign/eStamp, eNACH, dedupe and fraud controls, and versioned audit trails so compliance and internal audit have line of sight without extra steps.
This guide covers what LOS is (and isn’t), why traditional workflows stall MSME scale-up, how no-code configuration and APIs cut TAT and OPEX, which capabilities to insist on (data sources, underwriting engines, documentation orchestration, dashboards), and how to assess fit with core, risk, and compliance. The objective is clear: originate faster and more consistently, at a cost structure that makes MSME lending scalable.
What is Loan Origination Software?
Loan Origination Software is the digital backbone of modern lending. At its simplest, it manages the journey from the time an MSME applies for a loan until the credit line is sanctioned. But for Indian lenders, its role is far more critical – it replaces fragmented, manual steps with a unified, compliant, and data-driven process.
A robust LOS covers every stage of origination:
- Application intake: Capturing leads digitally across branches, DSAs, and online channels.
- KYC/KYB validation: Pulling data directly from CKYC, PAN, MCA, Udyam, and other public sources.
- Data ingestion: Automated access to GST filings, bank statements, bureau reports, and Account Aggregator feeds.
- Underwriting and decisioning: Rule engines and scorecards to evaluate borrower risk and calculate drawing power.
- Documentation and sanction: Auto-generation of loan agreements, eSign/eStamp execution, and audit-ready records.
For MSME lending in India, these capabilities matter because borrower profiles are highly diverse. Some are GST-registered with clean bureau histories; others rely on informal records or cash-based flows. An LOS gives lenders the ability to design different journeys for different borrower types while ensuring compliance with RBI requirements.
In short, LOS is not just about digitizing forms. It’s about creating a scalable, policy-driven origination engine that lets banks and NBFCs serve MSMEs profitably, without compromising speed, accuracy, or control.
Challenges in MSME Loan Origination Without Digital Platforms
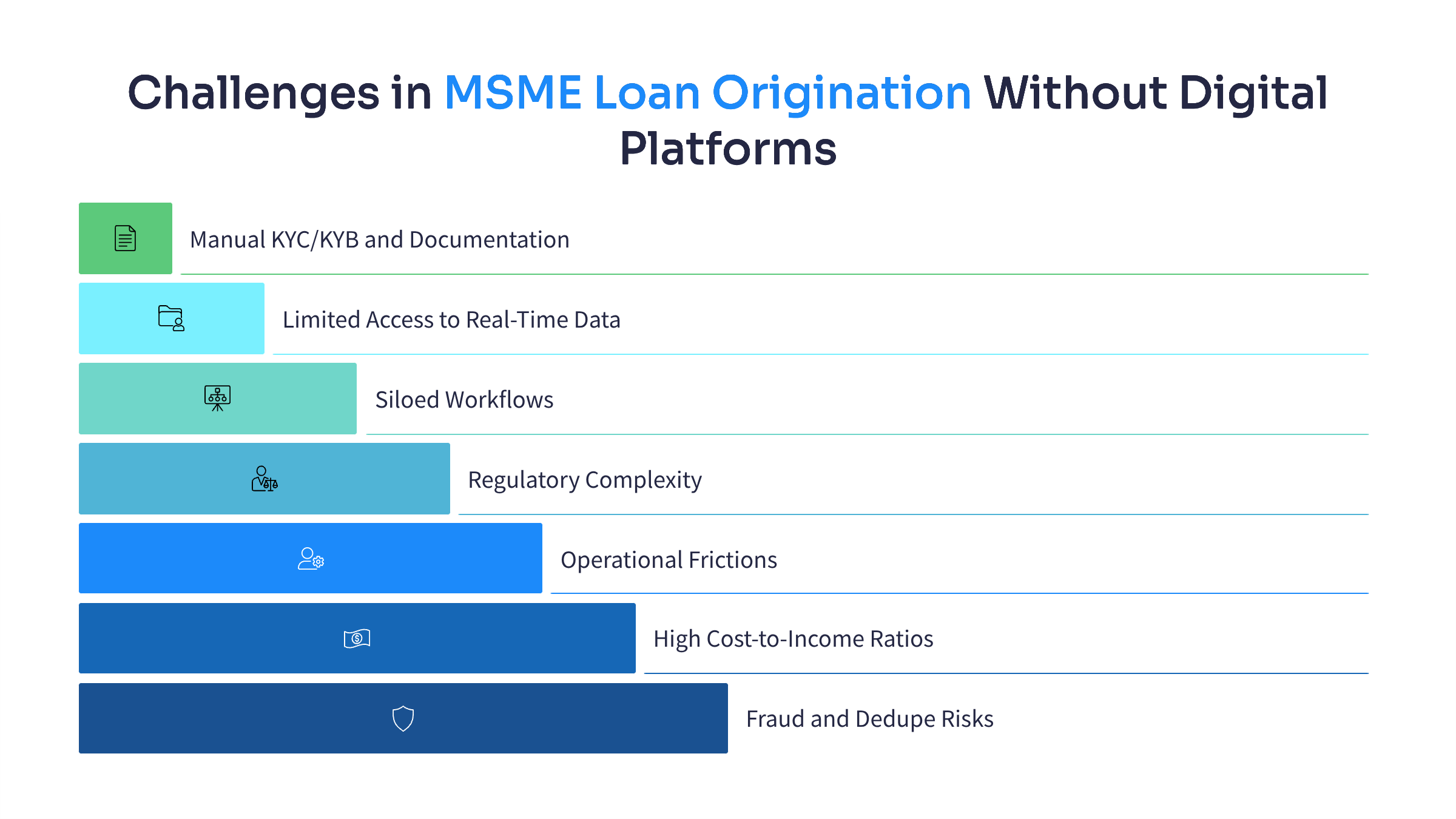
MSME lending in India carries both promise and complexity. While the market is vast, origination remains the hardest step to scale profitably. When banks and NBFCs rely on manual or semi-digital processes, the following challenges emerge:
- Manual KYC/KYB and Documentation
MSMEs often provide fragmented or inconsistent records across PAN, GST, Udyam, MCA, and bank statements. Without digital validation, lenders spend significant time resolving mismatches, increasing errors and compliance risk. - Limited Access to Real-Time Data
Underwriting depends on GSTN, bureau, and Account Aggregator feeds, but in manual setups data is often stale or incomplete. Borrowers moving in and out of e-invoicing thresholds add further variability. - Siloed Workflows
Sales, credit, compliance, and operations teams often operate on separate systems or spreadsheets. Each hand-off adds days to turnaround time, with no single source of truth for application status. - Regulatory Complexity
- Digital Lending Guidelines: Require full audit trails, disclosures, and control by regulated entities—difficult to enforce manually.
- Key Fact Statement (KFS): From Oct 2024, MSME loans must include standardized APR and fee disclosures; manual preparation creates high error risk.
- FLDG Caps and Co-Lending: New rules require file-level checks and reconciliations, which are cumbersome without automation.
- Operational Frictions
E-mandates, e-signatures, and e-stamping vary across states and banks. Handling them manually delays sanction and disbursement. - High Cost-to-Income Ratios
MSME loans are typically ₹5–50 lakh. When origination relies on physical documents and repeated checks, the cost per file rises sharply, making small-ticket loans unviable. - Fraud and Dedupe Risks
Duplicate applications across DSAs, synthetic identities, and mule accounts require real-time checks. Manual systems lack the controls to prevent leakage.
Together, these challenges explain why many lenders struggle to grow MSME portfolios sustainably. Without digital platforms, origination remains slow, costly, and exposed to compliance gaps.
Traditional MSME Loan Origination Process: Step-by-Step
For many Indian banks and NBFCs, MSME loan origination still follows a sequential, manual model. While each stage is essential, the way it is executed often slows down decision-making and raises costs.
- Lead Sourcing and Application
Applications come through branches, DSAs, or broker networks. Paper forms and scanned submissions create errors and delays in capturing borrower details. - KYC/KYB Verification
Borrower identity and business details are verified manually against PAN, GST, Udyam, MCA records, and physical documents. Missing or inconsistent information leads to repeated follow-ups and extended turnaround times. - Data Collection and Assessment
Underwriters request GST returns, bureau reports, and bank statements separately. Without automated ingestion from APIs or Account Aggregator feeds, data often arrives late or incomplete, delaying credit evaluation. - Credit Underwriting and Decisioning
Risk is assessed manually using spreadsheets and judgment calls. This slows down sanctioning, increases bias, and creates inconsistencies across underwriters. - Policy and Compliance Checks
Regulatory requirements such as exposure norms, KYC thresholds, Key Fact Statements (KFS), and co-lending reconciliations are tracked manually. Each step adds time and exposes lenders to compliance risk. - Documentation and Agreement
Loan agreements, stamp duty, eSign, and mandates are prepared offline or in partially digital systems. Different state and bank processes extend timelines further. - Disbursement
Once approvals are complete, funds are disbursed. Without integrated workflows, reconciliation and booking errors are common, especially in co-lending setups.
This linear, manual approach makes MSME loan origination slow, expensive, and difficult to scale, limiting lenders’ ability to meet market demand at the required speed and cost.
The Costs of Inefficient Loan Origination
When MSME loan origination remains manual, the consequences are significant, not just for lenders, but for borrowers and the wider economy.
- Slower Turnaround Times (TAT): Credit decisions that take weeks instead of days mean MSMEs lose access to working capital when they need it most. Many borrowers simply drop off or turn to faster competitors.
- Higher Operating Costs: Manual verification, repeated document handling, and siloed workflows increase the cost per loan. For small-ticket MSME loans, high operating costs quickly erode margins and make lending unprofitable.
- Missed Market Opportunities: Delays in origination mean lenders cannot respond quickly to seasonal spikes or anchor-led programs, leaving market share open to fintechs and more agile players.
- Compliance and Audit Risks: Manual processes make it harder to maintain consistent disclosures, exposure tracking, and audit trails. Non-compliance with RBI norms can lead to regulatory penalties.
- Weak Borrower Experience: For MSMEs, repeated paperwork and long wait times create frustration and mistrust, weakening relationships at a time when banks and NBFCs are seeking to expand into this segment.
How Modern Loan Origination Software Transforms MSME Lending
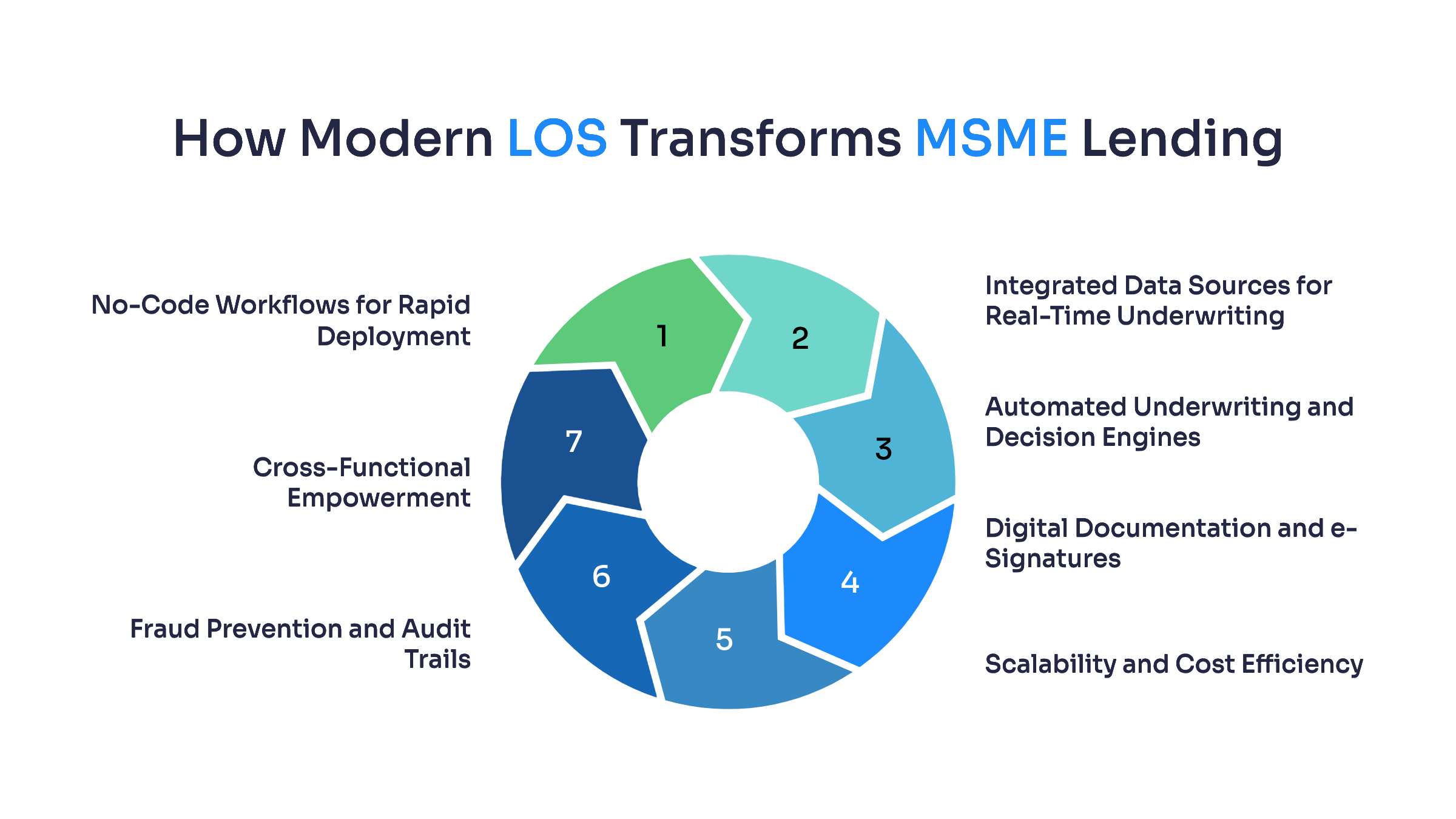
Modern Loan Origination Software is designed to handle the complexity of MSME lending at scale. By combining automation, integrations, and most importantly no-code configurability, it allows banks and NBFCs to originate loans faster, more consistently, and at a cost structure that makes small-ticket MSME credit viable.
- No-Code Workflows for Rapid Deployment
Traditional LOS requires coding and vendor dependency for every new journey or rule change. A no-code platform lets product, credit, and compliance teams configure borrower journeys directly, whether it’s onboarding for GST-registered MSMEs, rule-based credit scoring for thin-file borrowers, or anchor-led distributor programs. This agility means lenders can launch new MSME loan products in days instead of months.
- Integrated Data Sources for Real-Time Underwriting
MSME lending depends on multiple data streams. A modern LOS integrates these through APIs, pulling in fresh data automatically and reducing manual effort. Real-time ingestion enables dynamic drawing power (DP) calculations and cash-flow based underwriting, which are critical in MSME credit.
- Automated Underwriting and Decision Engines
Rule-based decisioning and customizable scorecards reduce reliance on manual judgment. With no-code engines, lenders can apply their exact policies such as segment-specific risk thresholds or sectoral exposure limits, while ensuring consistent decisions across underwriters. This speeds up sanctioning while strengthening governance.
- Digital Documentation and e-Signatures
Modern LOS embeds digital stamping, eSign, and eNACH mandates into the workflow. No-code templates make it easy to generate Key Fact Statements (KFS) and loan agreements that are audit-ready and aligned with RBI’s Digital Lending Guidelines. This cuts disbursement timelines and lowers compliance risk.
- Scalability and Cost Efficiency
Manual origination makes MSME loans unprofitable due to high cost per file. By automating repetitive checks (KYC, GST validation, bureau pulls) and eliminating paper-heavy processes, LOS reduces operating expenses. No-code flexibility means lenders can scale across geographies, borrower types, and ticket sizes without adding large teams.
- Fraud Prevention and Audit Trails
Deduplication, data validation, and anomaly detection are embedded into modern LOS. No-code design allows lenders to set fraud-control rules (e.g., duplicate PAN/GST detection, bureau dedupe) quickly. Every change in rules or workflows is logged in a version-controlled audit trail—ensuring both transparency and compliance.
- Cross-Functional Empowerment
No-code LOS platforms empower non-technical teams such as credit, risk, compliance, and business to collaborate without IT bottlenecks. Policy changes, new workflows, or compliance requirements can be operationalized immediately, reducing delays and dependency on long development cycles.
Benefits of Loan Origination Software for Indian Banks & NBFCs
For lenders, the value of a modern Loan Origination Software lies not just in digitization, but in how it reshapes the economics and risk profile of MSME lending. The key benefits include:
- Faster Turnaround Times (TAT)
Digital onboarding, automated data pulls, and rule-based decisioning reduce credit assessment from weeks to days, or even hours. Faster sanctioning improves borrower satisfaction and keeps anchors engaged in MSME-linked programs.
- Lower Operating Costs
Automation eliminates repetitive manual tasks such as KYC checks, GST validation, and document preparation. This significantly reduces cost per file, making even small-ticket loans viable at scale.
- Stronger Compliance and Governance
With embedded templates for Key Fact Statements (KFS), audit-ready logs, and version-controlled workflows, LOS ensures compliance with RBI’s Digital Lending Guidelines, FLDG caps, and co-lending requirements.
- Broader Market Reach
APIs and configurable workflows allow lenders to design differentiated journeys for vendors, distributors, dealers, and sub-dealers. This flexibility expands coverage across the MSME ecosystem, including thin-file or semi-formal borrowers.
- Consistent Credit Decisions
Rule engines and customizable scorecards apply policies uniformly, reducing bias and error. This improves portfolio quality and strengthens internal audit outcomes.
- Scalability and Innovation
No-code configurability enables rapid product launches – new schemes, borrower tiers, or anchor-specific workflows without waiting for IT builds. Lenders can respond quickly to regulatory changes, market shifts, or new partnerships.
Choosing the Right LOS for MSME Lending

Not all loan origination systems are created equal. For Indian banks and NBFCs, selecting the right LOS means looking beyond generic digitization to ensure the platform is tailored for MSME realities. Key factors to evaluate include:
- No-Code Configurability
The system should allow credit, risk, and operations teams to configure workflows, policies, and approval hierarchies without relying on long IT projects. This flexibility is crucial for anchor-led programs, product variants, or regulatory changes. - Comprehensive Product Coverage
A suitable LOS must support the full spectrum of MSME products, such as term loans, working capital (CC/OD), LAP, unsecured business loans, and supply chain finance (factoring, distributor finance, invoice discounting). This ensures lenders can scale across multiple product lines on a single, purpose-built. - End-to-End Digital Journeys
From borrower applications to sanction and booking, the LOS should provide digital onboarding, automated KYB/KYC, integrated GST/banking/bureau data, and e-sign/e-stamp capabilities. This reduces turnaround time while ensuring compliance. - Role-Based Modules
Look for modules that serve all stakeholders: borrower portals for MSMEs, DSA/sales interfaces, underwriter dashboards, and document management modules. Each group needs tools aligned to their tasks to reduce friction. - Integration and Security
Seamless APIs into core banking, CRM, and payment systems ensure smooth operations. At the same time, certified information security standards should be non-negotiable for handling sensitive MSME data.
Conclusion
MSME lending is a large, durable opportunity for Indian banks and NBFCs, but it won’t scale on manual origination. A modern Loan Origination Software changes the economics by digitizing onboarding, automating underwriting, and building auditability into every step.
CredAcc offers a no-code, API-first LOS built for India’s MSME context: configurable journeys for unsecured BL, LAP, working capital and SCF; role-based modules for borrowers, DSAs, and underwriters; embedded GST/banking/bureau data; and document, eSign/eStamp, and e-mandate orchestration – backed by microservices architecture and certified security (ISO 27001, SOC 2). Lenders use it to cut time-to-yes, lower cost-per-file, and launch product variants quickly, while staying audit-ready.
If you’re exploring ways to reduce TAT and improve unit economics in MSME origination, see how CredAcc’s no-code LOS can align policy, data, and operations on one platform.
Book a demo to review a live journey and configuration fit for your stack.

